- 10 Mar 2025
- 6 Minutes to read
-
Print
-
DarkLight
-
PDF
Executing a Playbook
- Updated on 10 Mar 2025
- 6 Minutes to read
-
Print
-
DarkLight
-
PDF
Overview
A Trigger is an event that initiates the actions defined within a Playbook in ThreatConnect®, which can vary depending on the type of Trigger used in the Playbook. This article covers how to execute Playbooks that use Mailbox, Timer, UserAction, WebHook, Group, Indicator, Intel Requirement, Case, and Victim Triggers.
Before You Start
User Roles
- To view Playbooks, your user account can have any Organization role.
- To execute Playbooks, your user account must have an Organization role of Standard User, Sharing User, Organization Administrator, or App Developer.
Prerequisites
- To execute a Playbook, you must first configure and activate the Playbook
- To have access to Playbooks, turn on the Playbooks system setting for your ThreatConnect instance on the System Settings screen (must be a System Administrator to perform this action).
Executing Playbooks
Playbooks With a Mailbox Trigger
Playbooks with a Mailbox Trigger execute when an email is received in the Trigger’s target mailbox. The email’s contents will then be passed along to any downstream Apps or Operators in the Playbook.
To test the functionality of an active Playbook that uses a Mailbox Trigger, click Send Email![]() at the top right of the Playbook Designer (Figure 1). Your computer’s default mail client will open a new message with the target mailbox address listed in the To: field. Alternatively, click Copy
at the top right of the Playbook Designer (Figure 1). Your computer’s default mail client will open a new message with the target mailbox address listed in the To: field. Alternatively, click Copy![]() to copy the target mailbox address to your computer’s clipboard so that you can paste it into an email message.
to copy the target mailbox address to your computer’s clipboard so that you can paste it into an email message.

Playbooks With a Timer Trigger
Playbooks with a Timer Trigger execute based on a set schedule (e.g., once a day, on the fifteenth of the month, etc.) defined in the Trigger’s Schedule and Daily Time parameters (Figure 2).
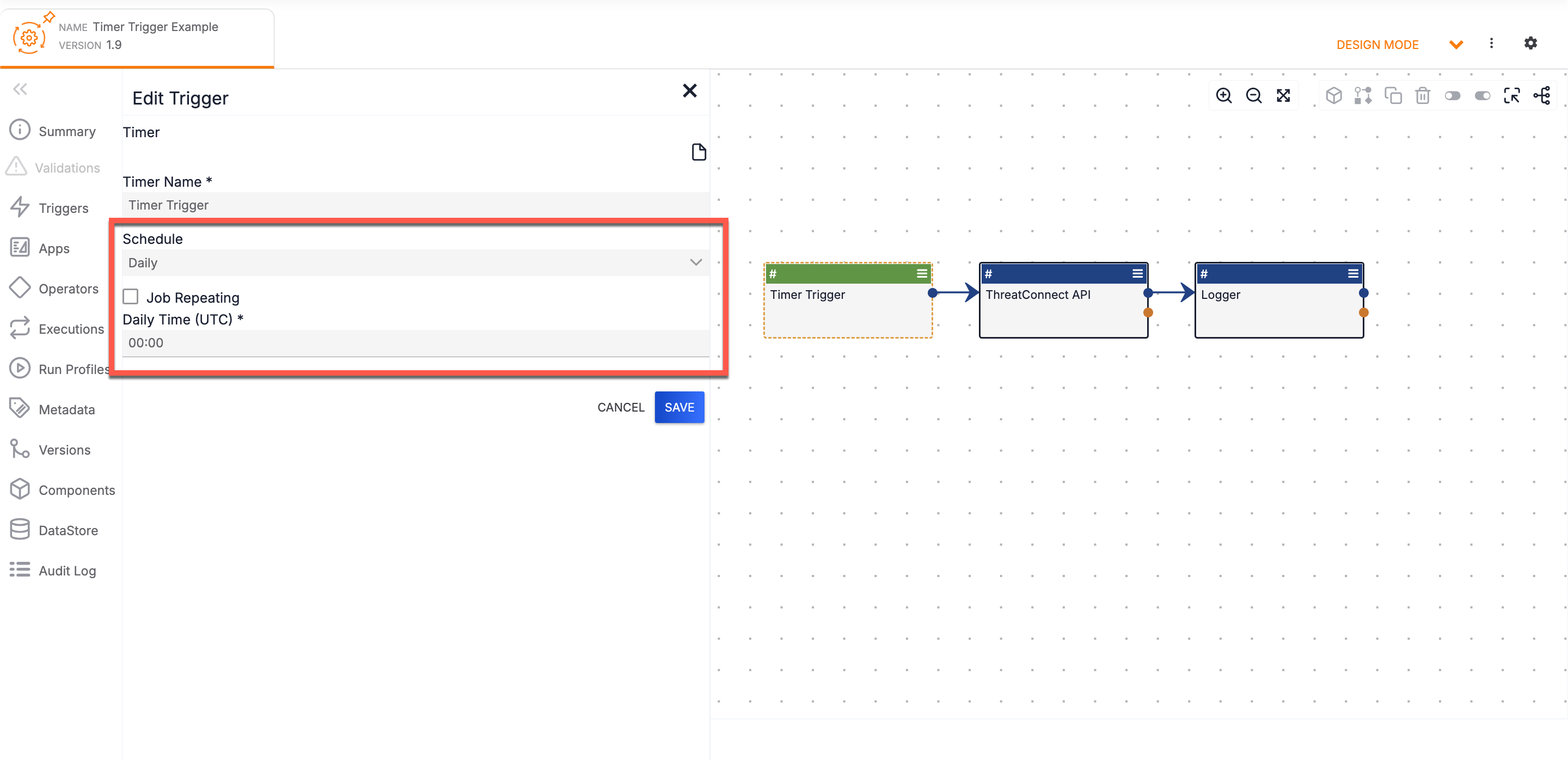
For example, if you set the Schedule parameter to Daily and the Daily Time parameter to 09:30, the Playbook will execute every day at 9:30 a.m. UTC. Note that the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) time standard is used when configuring the Daily Time parameter.
Playbooks With a UserAction Trigger
A UserAction Trigger lets you run Playbooks on demand while viewing the Details screen or drawer for Indicators, Intelligence Requirements, Groups, and Victims. You can also execute Playbooks with a UserAction Trigger configured for Indicators when using Threat Graph.
Details Screen and Drawer
On an object’s Details screen or Details drawer, the Playbooks card displays Playbooks with a UserAction Trigger configured for the object’s type (Figure 3). Click Run playbook![]() for a Playbook to execute it.
for a Playbook to execute it.
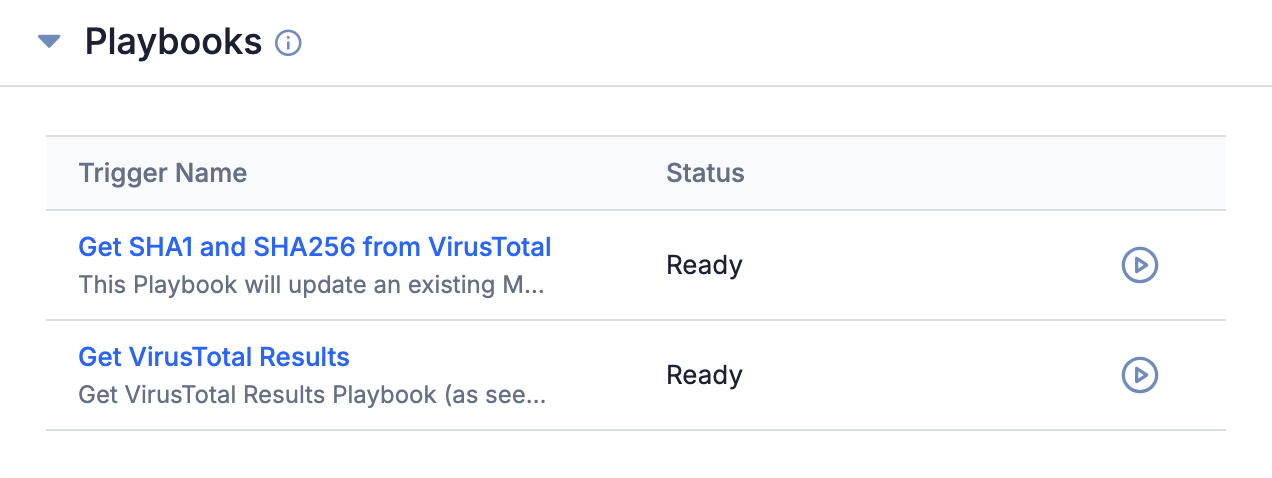
Depending on how the UserAction Trigger’s response body was configured, the Playbooks card will display the results of the Playbook’s execution in one of the following ways:
- If the Trigger contains a response body and its Render as Tip checkbox was selected, the Playbooks card will display the response body as a tooltip, along with a status of Complete in the Status column for the Playbook (Figure 4). If the tooltip closes, hover over the
 icon on the Playbooks card to display the tooltip again.
icon on the Playbooks card to display the tooltip again.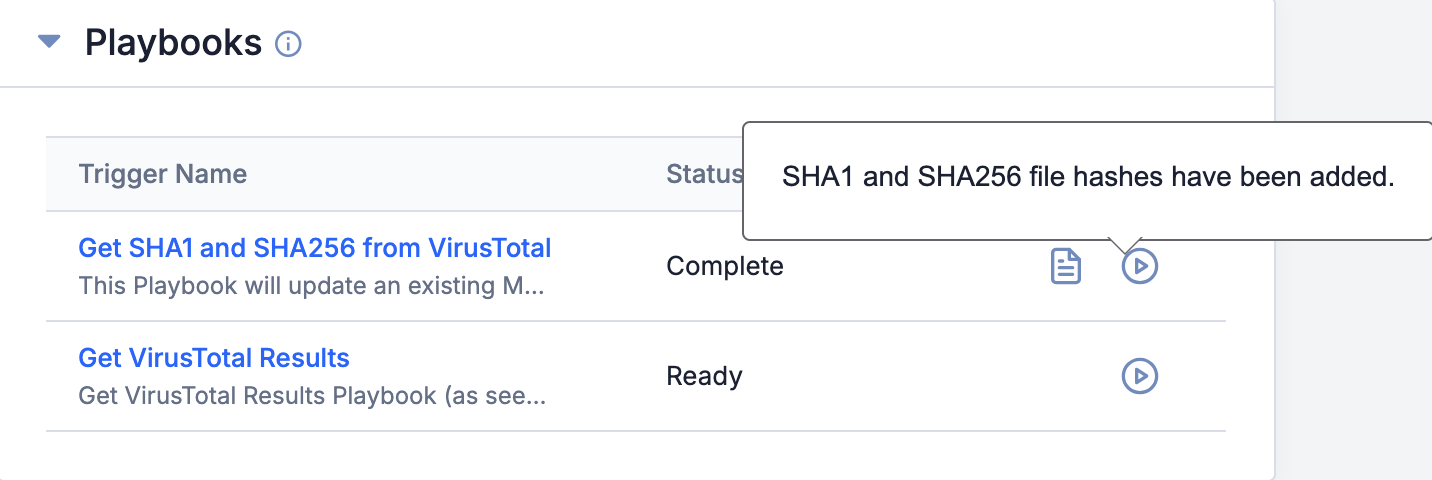
- If the Trigger contains a response body, but its Render as Tip checkbox was not selected, the Playbooks card will display only a status of Complete in the Status column for the Playbook; it will not display the Trigger’s response body.
- If the Trigger does not contain a response body, the Playbooks card will display a status of Complete in the Status column for the Playbook.
Legacy Details Screen
On an object’s legacy Details screen, the Playbook Actions card will be displayed on the Overview tab if there is at least one active Playbook with a UserAction Trigger configured for the object’s type (Figure 5). Click Run![]() for a Playbook to execute it.
for a Playbook to execute it.
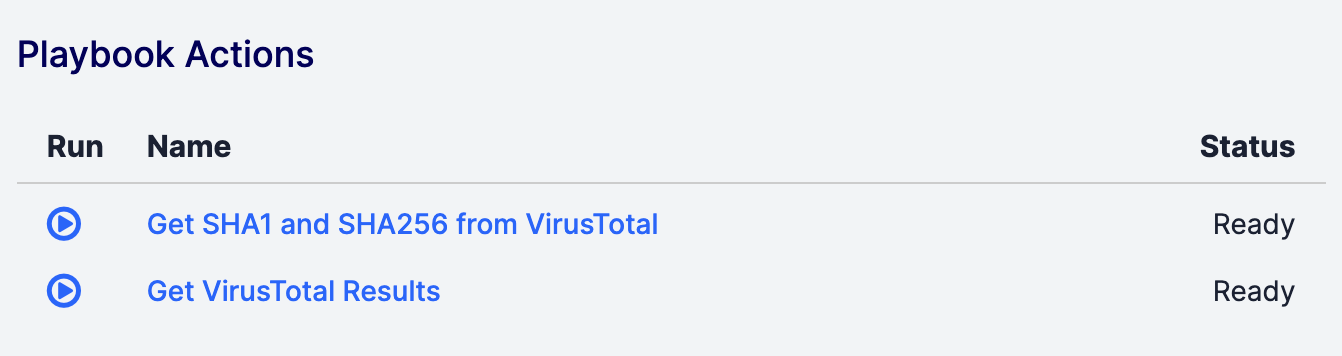
Depending on how the UserAction Trigger’s response body was configured, the Playbook Actions card will display the results of the Playbook’s execution in one of the following ways:
- If the Trigger contains a response body, but its Render as Tip checkbox was not selected, the Playbook Actions card will display the Trigger’s response body in the Status column for the Playbook (Figure 6).
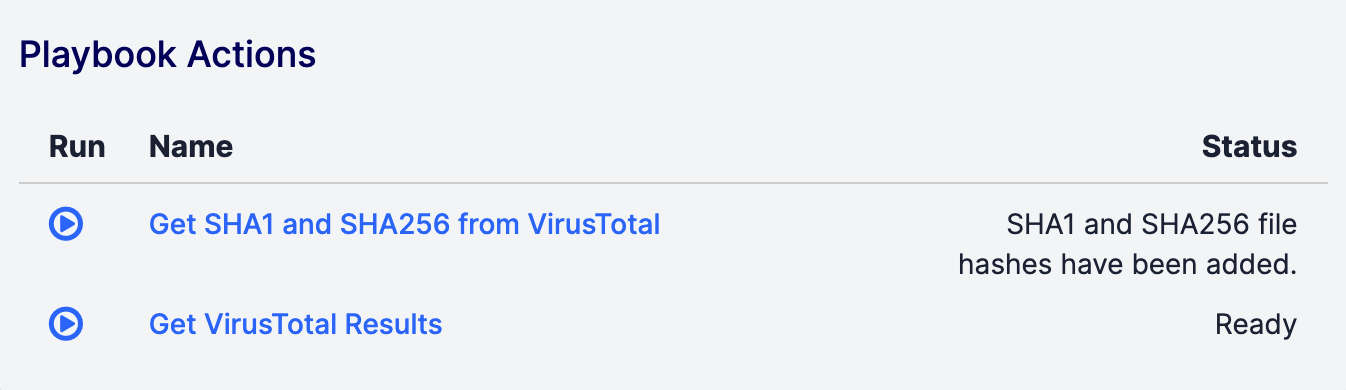
- If the Trigger contains a response body and its Render as Tip checkbox was selected, the Playbook Actions card will display the response body as a tooltip, along with a status of Completed in the Status column for the Playbook (Figure 7). f the tooltip closes, hover over Completed in the Status column to display the tooltip again.
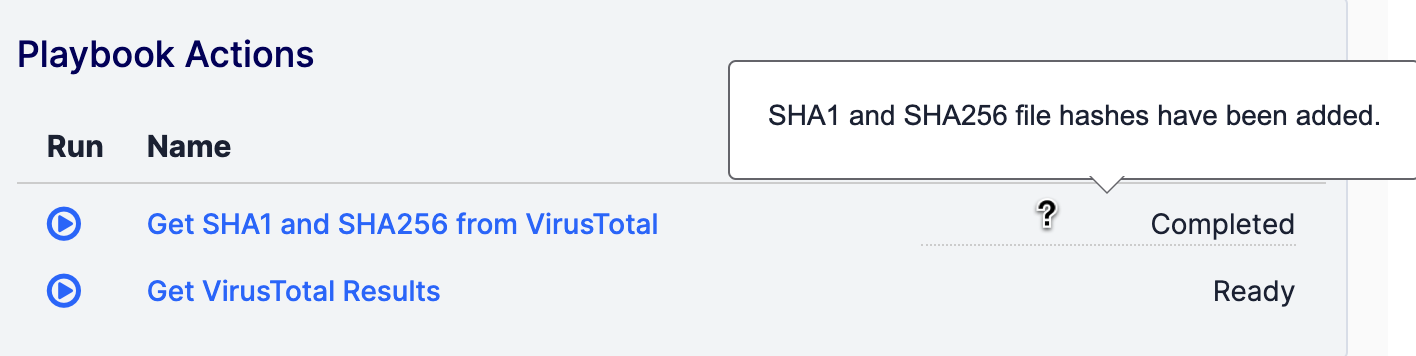
- If the Trigger does not contain a response body, the Playbook Actions card will display a status of Completed in the Status column for the Playbook.
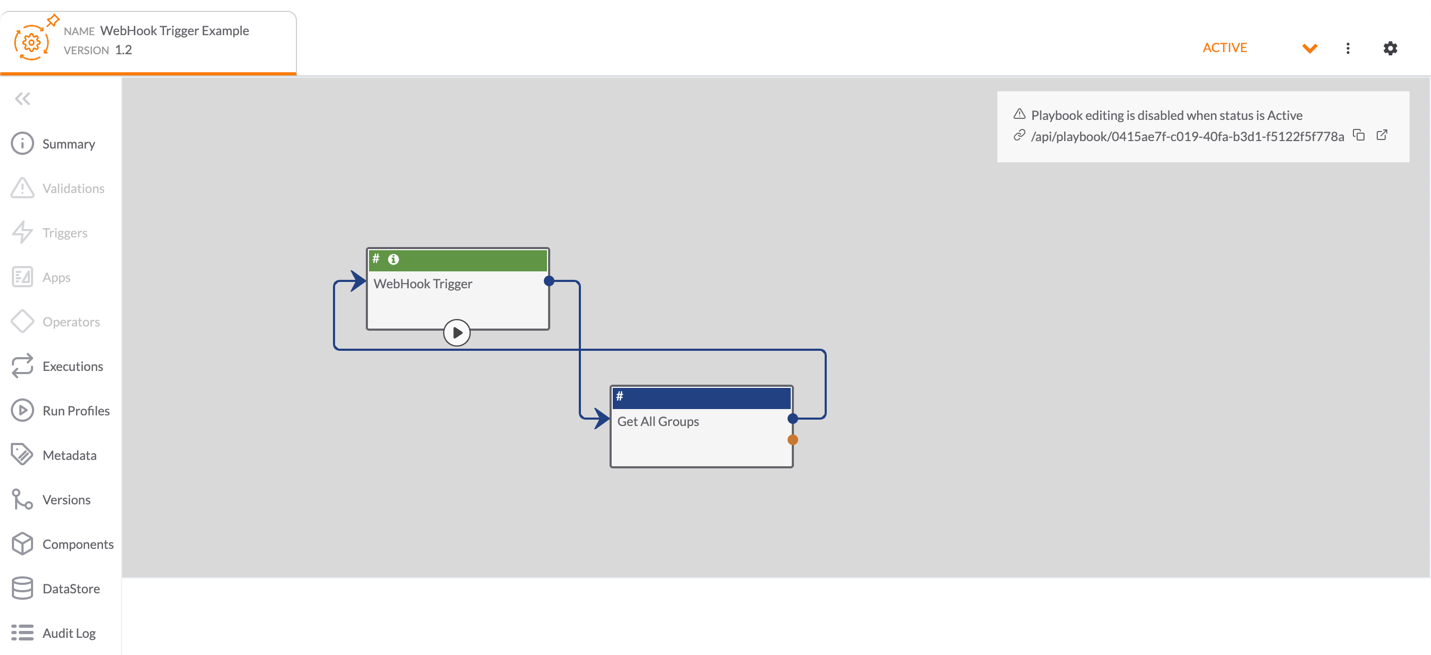
Playbooks With a WebHook Trigger
A WebHook Trigger creates an HTTPS endpoint that can process nearly any piece of information that can be sent via HTTP. To execute an active Playbook with a WebHook Trigger, click Execute Endpoint![]() at the top right of the Playbook Designer (Figure 8). Alternatively, click Copy Endpoint URL
at the top right of the Playbook Designer (Figure 8). Alternatively, click Copy Endpoint URL![]() to copy the endpoint URL and paste it into your browser’s search bar.
to copy the endpoint URL and paste it into your browser’s search bar.
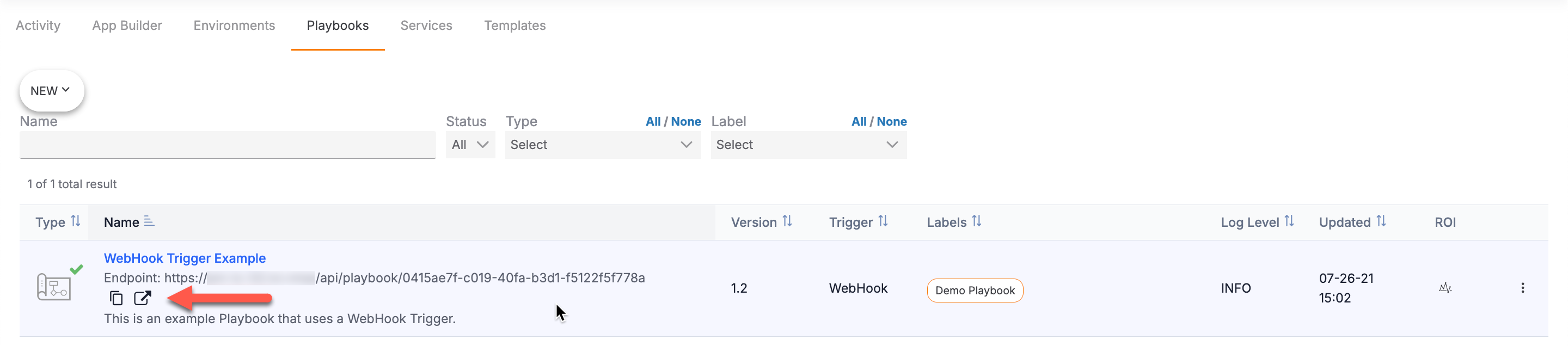
You can also access the Execute Endpoint![]() and Copy Endpoint URL
and Copy Endpoint URL![]() icons on the Playbooks screen by hovering over the table row for an active Playbook with a WebHook Trigger. Doing so will display both icons in the Name column, below the endpoint URL (Figure 9).
icons on the Playbooks screen by hovering over the table row for an active Playbook with a WebHook Trigger. Doing so will display both icons in the Name column, below the endpoint URL (Figure 9).
Playbooks With a Group, Indicator, Case, Intel Requirement, or Victim Trigger
Group, Indicator, Case, Intel Requirement, Track, and Victim Triggers represent the Group, Indicator, Case, Intelligence Requirement, and Victim objects in ThreatConnect, respectively. Playbooks that use any of these Triggers will execute when a particular action is taken on an object of the type represented by the Trigger, based on how you configured the Trigger’s Owners and Action Type parameters (Figure 10). For example, a Playbook with a Host Trigger can be configured to execute when a new Host Indicator is created in your Organization and/or one or more of your Communities or Sources, and a Playbook with a Case Trigger can be configured to execute when the severity for a Workflow Case in your Organization has been set.
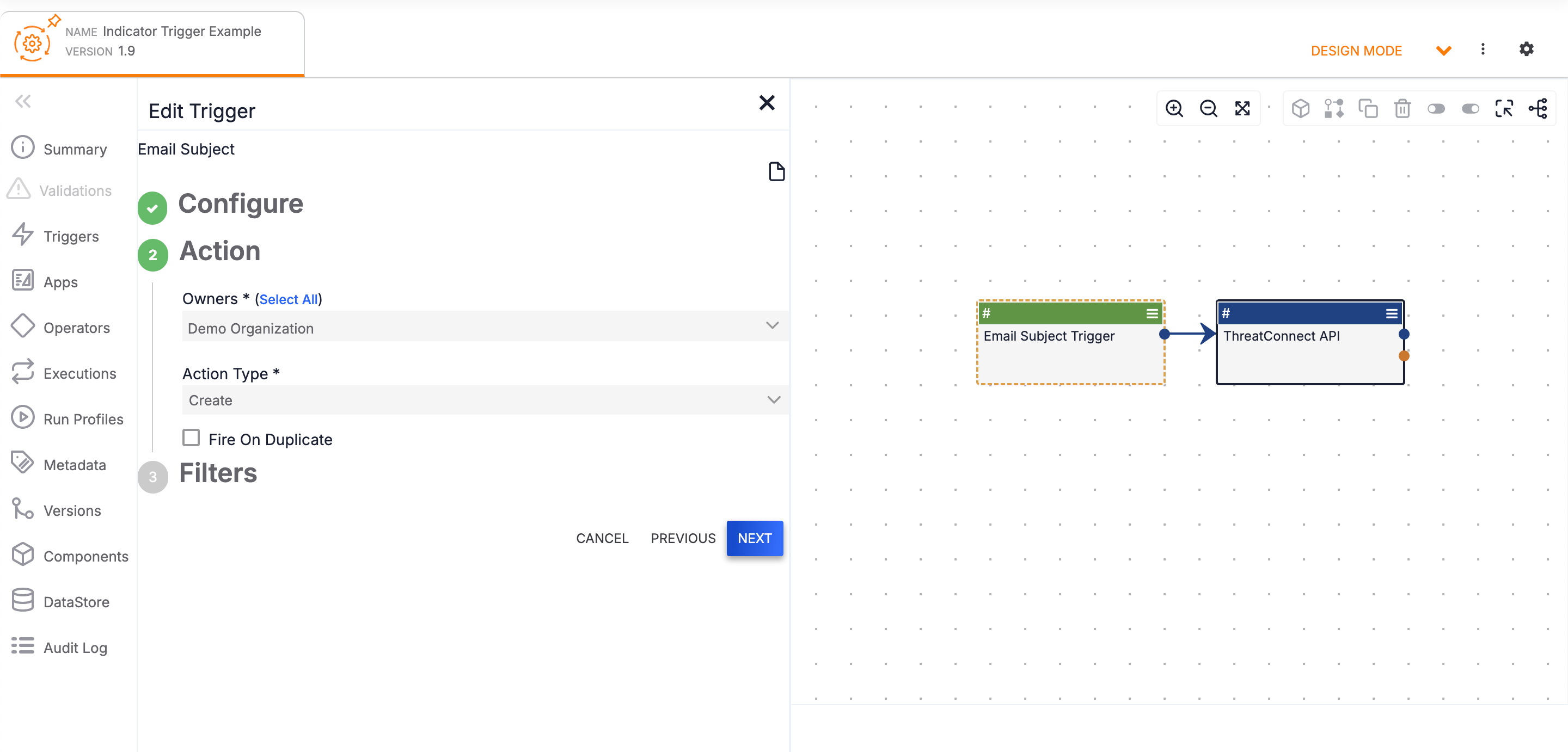
The Owners parameter determines the ThreatConnect owners in which the Playbook can be executed. You must select at least one owner when configuring the Trigger.
The Action Type parameter determines the action the Trigger will listen for. When the selected action takes place in one of the specified owners, the Trigger will start the Playbook. For example, if an Email Subject Indicator Trigger is configured with Create as its Action Type and Demo Organization as its Owner, the Trigger will start the Playbook whenever an Email Subject Indicator is created in the owner named Demo Organization.
See Table 1 for a list of values for the Action Type parameter and the supported Trigger types for each value.
| Value | Supported Trigger Types |
|---|---|
| Create | Case, Group, Indicator, Intel Requirement, Victim |
| Delete | Case, Group, Indicator, Intel Requirement, Victim |
| New Results | Intel Requirement |
| Security Label Applied | Group; Indicator, Victim |
| Security Label Removed | Group; Indicator, Victim |
| Set Resolution | Case |
| Set Severity | Case |
| Specific Status Set | Case |
| Tag Applied | Case, Group, Indicator, Intel Requirement, Victim |
| Tag Removed | Case, Group, Indicator, Intel Requirement, Victim |
Playbooks With a Service Trigger
Service Apps are microservices that constantly run in the background. Executing a Playbook that uses a Trigger Service will vary based on how you configure the Trigger Service and its corresponding Playbook Trigger. See Playbook Services for more information on creating Trigger Services.
Stopping Playbook Executions
You can stop Playbook executions from the Executions pane of the Playbook Designer. See the “Stopping a Playbook Execution” section of Playbook Executions for more information.
ThreatConnect® is a registered trademark of ThreatConnect, Inc.
20115-01 v.04.B


