- 20 Aug 2025
- 8 Minutes to read
-
Print
-
DarkLight
-
PDF
CAL 3.13 Release Notes
- Updated on 20 Aug 2025
- 8 Minutes to read
-
Print
-
DarkLight
-
PDF
CAL Doc Analysis Service Improvements
ThreatConnect®’s MITRE ATT&CK® AI classification feature, part of the CAL™ Doc Analysis Service, can now identify 90% of all MITRE ATT&CK techniques and sub-techniques from implicit mentions in Reports in the CAL Automated Threat Library (ATL) Source, bringing the number of techniques and sub-techniques it can recognize to 608. This extra level of analysis and extraction provides even more information and insights to help you better understand your adversaries.
What can AI-based identification of 608 MITRE ATT&CK classifications do for your workflows?
- Identify Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) not explicitly called out in Reports
- Identify four times the number of MITRE ATT&CK tactics and techniques identified by traditional matching methods
- Prioritize the most essential Reports, based on identified TTPs
- Save time by removing irrelevant content from queries and Intelligence Requirements (IRs)
- Support more visual and informed exploration within ThreatConnect’s ATT&CK Visualizer and Threat Graph
ThreatConnect Feature | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAL Doc Analysis Service Feature | Description | Doc Analysis Import | ThreatConnect Intelligence Anywhere Browser Extension | ThreatConnect Doc Analysis Playbook App | CAL Automated Threat Library Source |
| Alias Extraction | Extracts explicit MITRE ATT&CK Enterprise techniques, sub-techniques, tactics, malware, tools, intrusion sets, and courses of action, as well as Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), from the provided content. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| IOC Extraction | Extracts explicit indicators within the content, including addresses, email addresses, file hashes (MD5, SHA1, and SHA256), Hosts, URLs, ASNs, and CIDRs. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| MITRE ATT&CK AI Classification | Classifies CAL ATL Report text identified as MITRE ATT&CK techniques and sub-techniques. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| CAL ATL Report AI Summarization | Uses an artificial intelligence (AI) large language model (LLM) to summarize reports into 200-word summaries and three to five bullet points. | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| NAICS AI Industry Classification | Uses NAICS AI industry classification to categorize subsector-related industries and their corresponding sectors based on the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS) framework. | ✔ | ✔ | ||
| AI Exploited-Vulnerability Analyzer | Examines CAL ATL Reports for specific qualities to determine whether the content is likely about a zero-day or exploited vulnerability and, if so, to add a vulnerability-specific Tag and customize the AI summary for key vulnerability-focused details. | ✔ | |||
CAL Doc Analysis Alias Extraction Updates
The CAL Doc Analysis Service now uses improved logic to prevent objects with names/summaries or descriptions that include overly common words from being extracted when they match with, but are not actually pertinent to, known aliases of threat actors, tools, or malware. This change reduces the chance of Reports being misclassified due to generic phrases like “Silicon Valley” or “Apple Silicon,” which previously matched threat actor aliases such as “Silicon” for groups like “Sea Turtle.”
This update improves the precision of automated tagging by filtering out common-word aliases during analysis. It also reduces the chance that features like Doc Analysis Import, the ThreatConnect Intelligence Anywhere browser extension, the ThreatConnect Doc Analysis Playbook App, and the CAL Automated Threat Library Source will return false positives, allowing you to spend more time focusing on relevant, high-confidence intelligence.
CAL Indicator Enrichment
CAL is ThreatConnect’s global intelligence engine that transforms insights into action—enriching Indicators, enhancing context, and enabling 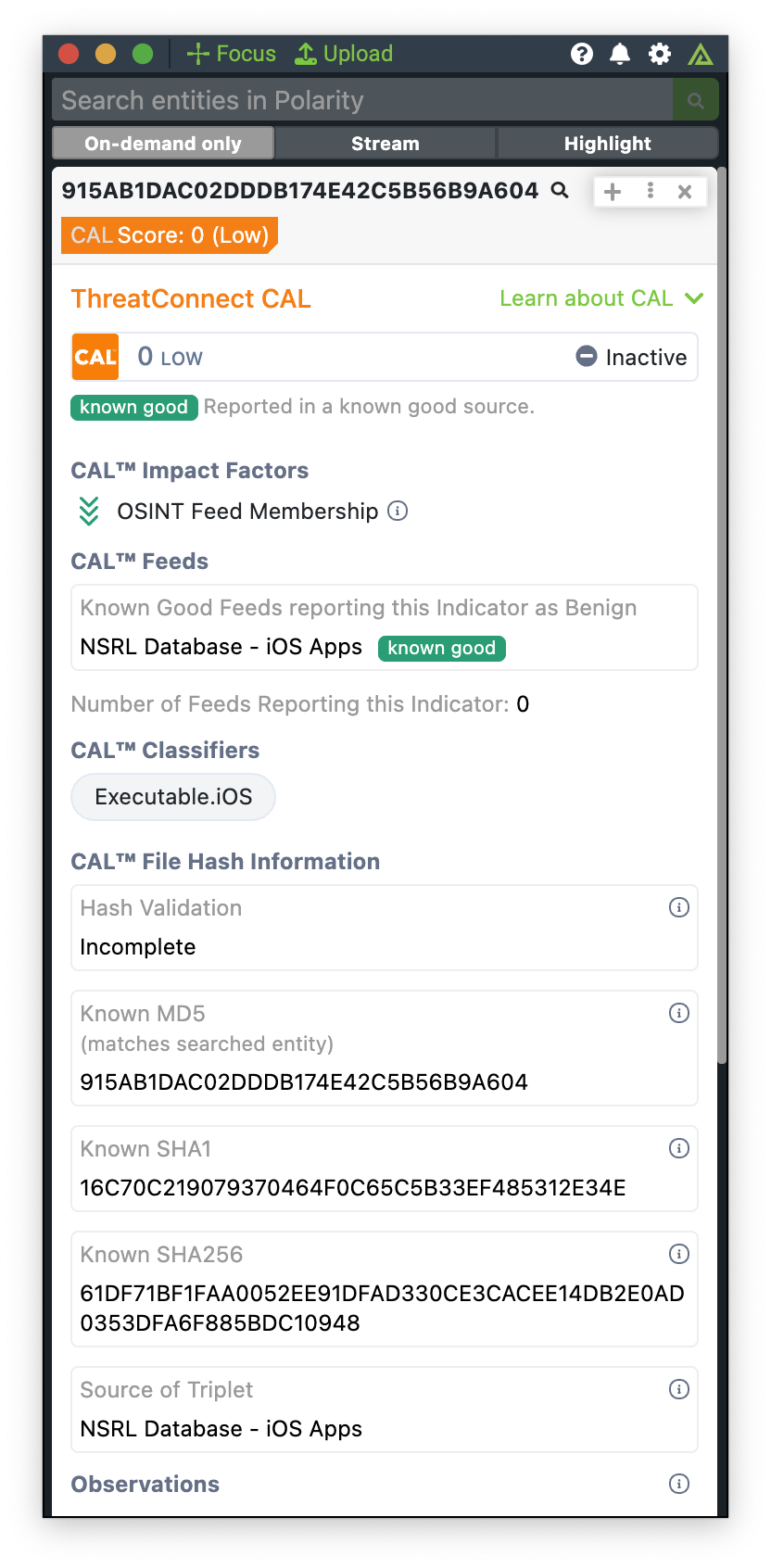 smarter threat decisions across the cyber threat intelligence (CTI) lifecycle. From ingestion to enrichment, CAL connects the dots between billions of Indicators, adversary behaviors, community observations, and your team’s real-world needs. It delivers high-fidelity, real-time analytics that power everything from Playbooks to browser extensions, IR enrichment workflows, and AI-driven classification features.
smarter threat decisions across the cyber threat intelligence (CTI) lifecycle. From ingestion to enrichment, CAL connects the dots between billions of Indicators, adversary behaviors, community observations, and your team’s real-world needs. It delivers high-fidelity, real-time analytics that power everything from Playbooks to browser extensions, IR enrichment workflows, and AI-driven classification features.
At the heart of CAL is an ever-evolving dataset of over 2.2 billion global Indicators and 267+ billion data points drawn from open-source intelligence (OSINT), community telemetry, and proprietary sources. Each Indicator is dynamically scored using 14 weighted impact factors such as malware associations, blocking behavior in feeds, and community observations. These enrichments are delivered in milliseconds—both through the ThreatConnect user interface and directly into tools like Polarity, which analysts can use to pivot on and prioritize data without switching context.
NSRL Enrichment
With the latest update, CAL has integrated 47.8 million new “Known Good” hashes from the National Software Reference Library (NSRL)—a National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)–supported initiative backed by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to assist in identifying benign software during criminal investigations. This expanded coverage spans PC, Android™, and iOS™ platforms.
For analysts, this update translates directly into greater speed, clarity, and confidence during investigations. CAL’s integration with NSRL enables near-instant identification of benign, traceable software artifacts, allowing teams to focus their energy on unknowns and actual threats. Whether analysts respond to incidents, review threat reports, or build detection logic, this enrichment layer helps streamline workflows, minimize alert fatigue, and ensure higher fidelity in threat assessments. These enrichments are now available via the Get CAL Enrichment Playbook App, the Details screen for Indicators, and the ThreatConnect CAL integration for Polarity, bringing known-good intelligence exactly where analysts need it.
New CAL ATL Sources
ThreatConnect's CAL Automated Threat Library (ATL) Source transforms how cyber threat intelligence teams extract value from OSINT. Designed to supercharge your investigations with curated, machine-readable insights, CAL ATL automatically ingests blogs and reports from authoritative security sources and enriches them using AI-powered analytics, reducing noise and surfacing what matters most. Whether you're looking to understand emerging TTPs, identify high-risk vulnerabilities, or rapidly pivot across intelligence objects, CAL ATL provides structured, actionable context—directly within the ThreatConnect platform.
The following blogs have been added to the CAL Automated Threat Library Source with the CAL 3.13 release:
- Bellingcat: Publishes detailed investigative reports, from disinformation campaigns to cyber espionage cases. Bellingcat, a leader in open-source investigations and verification, also curates tools and methodologies used by OSINT researchers in areas such as network analysis, geolocation, and social media tracking. Analysts can draw on Bellingcat for attribution reference, geopolitical context, and verification techniques.
- Cyberscoop: Public-sector media company that delivers breaking cyber security news.
- Cyberscoop Attacks: Focuses on breaking news about actual cyber incidents, such as intrusions, ransomware outbreaks, and breach disclosures.
- Cyberscoop Threat Defense: Examines technology, policy, and defense operational perspectives—sharing insights on regulations, CISO strategy, and incident response innovation.
- Cyberscoop Security Strategy: Provides commentary and analysis on national policy, intelligence strategy, and tactical defense alignment across industry and government.
- Google Project Zero: Publishes reports by an elite team of researchers employed by Google® on zero‑day vulnerabilities across major software platforms. Recent policy updates commit to earlier public disclosure to reduce the “upstream patch gap,” and AI‑augmented tools like Google’s Big Sleep are now uncovering bugs autonomously. This source enables CAL ATL users to stay ahead of exploit chains and vendor patch timelines.
- HACKMAGEDDON: Provides granular cyber attack timelines and statistics, aggregating hundreds of events per period and categorizing them by motivation (e.g., cybercrime, espionage) and technique (e.g., malware, ransomware, exploitation). HACKMAGEDDON’s timely insights can supplement an analyst’s efforts to identify change in attacker behavior trends over time.
- HackRead: Covers global information security news, cybercrime, privacy, surveillance, and hacking events. A fast-moving independent platform, HackRead often breaks stories on criminal infrastructure and enables early detection of trending threat narratives and tool proliferation.
- Schneier on Security: Provides high-level analysis on security policy, cryptography, privacy, and the societal impacts of cyber risk. Active since 2004, Bruce Schneier writes essays and a monthly Crypto-Gram newsletter that explore how politics, regulation, and technology intersect—critical for analysts tracking nation-state activity and regulatory landscapes.
- Seqrite: Provides threat research, attacker reports, and insights into malware campaigns, particularly targeting small and midsize businesses (SMBs) and critical industries in Asia. Published by Seqrite™, a security vendor brand, this blog offers practical, hands-on threat insight with regional specificity that can enhance early warning coverage.
- Sophos and Sophos Threat Research: Publish deep-dive blogs on advanced threats such as ransomware, zero-day attacks, and malware tactics. The Sophos® research team regularly publishes detailed analyses of active campaigns, including Internet of Things (IoT) attacks and crypto-based malware. These posts offer actionable technical details and detection strategies valuable for threat hunters and SOC teams.
- TechTarget Search Security: Delivers award‑winning technical how‑tos, news, and feature content—from risk management to threat detection and cloud security—aimed at audiences across technical levels, from security analysts to CISOs. For CAL ATL, this blog from TechTarget® provides structured guidance and timely trend reporting to bolster tactical and strategic threat intelligence workflows.
- TechXplore: Publishes cybersecurity research updates—especially on threats driven by emerging fields like AI, robotics, and hardware vulnerabilities—adding modern scientific context to intelligence reporting. This reporting is in addition to TechXplore™’s primary focus on the broader tech landscape.
- The Cyber Express Daily Firewall: Tracks the latest threats, breaches, dark-web activity, and firewall trends, delivering concise and up-to-date alerts. A daily feature from The Cyber Express by Cyble™, this flagship news feed’s focus on network defense technology and emerging attack vectors makes it an essential tactical layer.
Other Updates
- CAL ATL blog retirement: Dark Reading and The DFIR Report were retired from CAL ATL due to vendor blocking.
- CAL ATL missing Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) Reports: In specific situations, CISA’s RSS feed did not update the timestamp for reports, leading to some alerts not being added to CAL ATL. The ThreatConnect CAL Team has put a workaround in place to handle this situation.
- CAL ATL not creating specific CVEs: The ThreatConnect CAL Team identified some logic applied to CVEs found in CAL ATL Reports that prevented the Vulnerabilities from being created if they were not already in the CAL data set. The update allows them to be created.
- CAL Safelist: CAL 3.13 provides a significant update to the CAL Safelist that includes 397 new entries, preventing 6.2+ million Indicators from cluttering analysts workflows. The Safelist improves response times and minimizes alert fatigue in automated workflows and analyst queries by marking non-IOCs as inactive.
- Whois Indicator enrichment stability improvements: These improvements affect the Whois Indicator enrichment that happens in several areas of ThreatConnect, including CAL newly registered domain (NRD) feeds, Host DNS enrichment prioritization that affects parts of CAL scoring and status, CAL Classifiers (Host.WHOIS.Expired, Host.WHOIS.LongRegistration, and Host.WHOIS.ShortRegistration), and some CAL relationships in Threat Graph. Note that this is not the same service that powers the Whois registration lookup feature on a Host Indicator’s Details screen. That service is not affected by this update.
ThreatConnect® is a registered trademark, and CAL™ is a trademark, of ThreatConnect, Inc.
TechXplore™ is a trademark of Booz Allen Hamilton, Inc.
iOS™ is a trademark of Cisco Systems, Inc.
The Cyber Express by Cyble™ is a trademark of The Cyber Express LLC.
Google® is a registered trademark, and Android™ is a trademark, of Google LLC.
MITRE ATT&CK® and ATT&CK® are registered trademarks of The MITRE Corporation
Seqrite™ is a trademark of Quick Heal Technologies Limited.
Sophos® is a registered trademark of Sophos Limited.
TechTarget® is a registered trademark of TechTarget, Inc.


